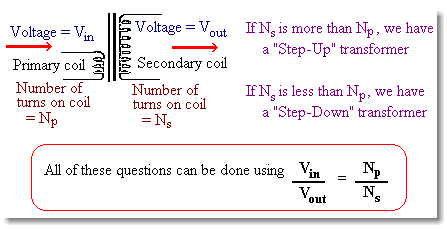Posted by : admin
Thursday, 20 November 2014
Transformer is an electrical device which transfers
electrical power from one coil (primary) to another (secondary) by the
principle of mutual induction. The input is given through the primary and the
output is tapped from the secondary.
If the secondary coil has more number of turns than that of the primary it is called "STEP UP" transformer. Because , the secondary voltage will be more than that of the primary voltage. If it is the other way it is called "STEP DOWN" transformer. Here the secondary voltage will be less than that of the primary.
In an ideal transformer, the power input will be equal to the power output. But practically it is impossible due to certain transformer losses.
Actually the transformer increases or decreases the voltage. So the current will be inversely proportional. ie. if the voltage is increased current will be decreased. and vice versa.
If the secondary coil has more number of turns than that of the primary it is called "STEP UP" transformer. Because , the secondary voltage will be more than that of the primary voltage. If it is the other way it is called "STEP DOWN" transformer. Here the secondary voltage will be less than that of the primary.
In an ideal transformer, the power input will be equal to the power output. But practically it is impossible due to certain transformer losses.
Actually the transformer increases or decreases the voltage. So the current will be inversely proportional. ie. if the voltage is increased current will be decreased. and vice versa.
Difference between step-up
transformer and voltage amplifier
Than a very strange but thinkable question comes what is the difference between the two and can we use a small step up transformer in place of voltage amplifier and vice-versa?
Differences
|
Transformer
|
Amplifier
|
|
Transformers are unable to amplify (step up) an ac input
Voltage without reducing (stepping down) it`s current capability.
|
Amplifier can amplify both current and Voltage at the same
time. We can have 1V at 1uA to drive the input but might also get many volts
at many Amps at the output.
|
|
Transformer`s coil windings never requires a dc Voltage to
operate. Sometimes a dc Voltage might be present in a transformer winding for
auxiliaries but the dc is not required for the operation of the transformer.
|
Amplifier almost always requires a dc working supply
Voltage to operate.
|
|
Transformer has more winding added to its secondary
winding to obtain Voltage amplification.
|
An Amplifier actually modulates a fixed dc source Voltage
in response to an ac input Voltage to obtain output Voltage amplification.
|
|
A transformer`s input current is proportional to its load
current.
|
Amplifier’s input current is normally almost independent
of its load current.
|
|
A transformer is like a gearbox, whereas an amplifier is
like an engine. The gearbox converts energy like a transformer.
|
Amplifier is like an engine, which consumes fuel to give
output. Similarly amplifier consumed DC supply to give output.
|
|
A step up transformer can amplify a specified type of
input which is the sinusoidal input or time varying input and add to that the
range of input the transformer is very flexible in range.
|
Amplifier can amplify any signal and while the amplifier
would have a limited range then in the saturation state.
|
|
In an ideal transformer output impedance is equal to the
source impedance times the square of the turns ratio.
|
An amplifier can have output impedance that is independent
of the source impedance.
|
Rule for a Step-Up Transformer
Electrical Codes
·
Under the National Electrical Code, a step-up
transformer must have certain current carrying protections in place. There must
be a main circuit breaker installed in a load center served by the transformer,
and the main breaker can be no larger than 70 percent of the maximum current
capacity of the transformer.
KVA Rating
·
All transformers have a KVA rating. This rating
represents the transformer's maximum capacity in kilowatts (thousands of
watts). In calculating what KVA means in practical terms, Watt's Law is
applied. In Watt's Law, power (P) equals the output voltage (E) times the
ampere capacity (I). Using this formula, P = E x I, and its direct derivatives,
I = P / E and E = P / I, all transformer attributes can be calculated. For
example, if the transformer's rating is 10 KVA and has a 240-volt output, it
has a current capacity of 41.67 amperes (10,000 watts / 240 volts = 41.67
amps).
Application
·
Watt's Law also applies when choosing a step-up
transformer for an application. If a transformer needs to step-up 240 volts to
480 volts, and you need a maximum current capacity of 40 amps, you must first
calculate the number of amps needed to comply with electrical codes. If the
codes require a maximum usage of 70 percent of the transformer's capacity,
multiply 40 times 1.43. The product will be 57.2 amps, 70 percent of which is
40.0 amps. Knowing you need 57.2 amps (I) and the output of 480 volts (E)
Watt's law can be applied as P = I x E. Therefore, 57.2 x 480 = 27,456 watts,
or 27.456 KVA. This would be the minimum size transformer required for this
application
How Calculate turn ratio on step up transformers?
For example: if the primery winding on the transformer were 250 turns and the 1250 turns on the secondary, what is the turn ratio? Well what you do is you take 1250 divide that by 250 will give you 5. So the answer would be 1:5 since 1 will be on the top of the 250 and the 5 would be on the top of the 1250. IN ALL STEP UP TRANSFORMERS HAVING A TURNS RATIO MORE THAN ONE...BECAUSE IT STEPS UP VOLTAGE.
Step up Transfromer Calculation
Related Posts :
- Back to Home »
- Define , transformer , transformer calculation , transformer videos »
- step up transformer Define,working and calculation